📜 要約
### 主題と目的の要約
本調査は、「自治体におけるAIの政治利用事例の調査と比較分析」をテーマに、AI技術が地方自治体の政策決定や公共サービスに与える影響を探求することを目的としています。特に、AIの導入が市民の信頼に与える影響や、成功事例と失敗事例を通じて、どのようにAIが公共政策に組み込まれているかを明らかにすることを目指しています。
### 主要な内容と発見
調査の結果、AIの導入は公共政策において増加しているものの、市民の信頼を損なうリスクがあることが明らかになりました。具体的な事例として、トロント市の「スマートシティ」プロジェクトや英国の教育省のAIアルゴリズムによる試験成績予測の中止が挙げられ、これらは市民の懸念を反映しています。また、成功事例としてサンタクルーズ郡やボストン市の取り組みがあり、特にサンタクルーズ郡は他の自治体のモデルとなることが期待されています。一方で、ミシガン州の失業保険機関のエラーやカリフォルニア州とコロラド州でのメディケイドの誤拒否といった失敗事例は、AIシステムの透明性や公平性の重要性を示しています。
### 結果と結論のまとめ
調査の結果、AIの導入には成功を収めるための戦略と失敗を避けるための慎重なアプローチが求められることが確認されました。AIは地方政府における公共サービスの提供や市民とのコミュニケーションを改善する可能性を持つ一方で、適切な管理がなされない場合には公共の信頼を損ない、社会的不平等を強化するリスクがあることも指摘されました。したがって、AIの導入に際しては、倫理的な考慮や透明性が重要であり、政府機関は責任あるAIの使用を推進する必要があります。
🔍 詳細
🏷 AIの導入と政治的意思決定への影響
#### AIの導入と政治的意思決定への影響
AIの導入が公共政策に与える影響についての研究では、政府機関がAIを用いて政策決定を行うことが増加している一方で、市民の信頼を損なう懸念が高まっている。実験的調査によると、AIに関する情報提供が市民の態度に大きな影響を与えることが示され、特にポジティブな情報はAIの使用に対する支持を高める傾向がある。具体的な事例として、トロント市の「スマートシティ」プロジェクトや英国の教育省のAIアルゴリズムによる試験成績予測の中止が挙げられ、これらは市民の懸念を反映している。結論として、AIの公共政策への導入においては、情報提供が市民の理解と支持を促進する重要な要素であることが強調されている。
#### AIを公共政策に活用する政治的側面
政府機関がAIを用いて重要な政策決定を行うことが増えているが、これに対する反発が強まっている。特に、AIの導入が公共の信頼を損なう可能性が懸念されている。研究目的は、公共政策におけるAIの使用に対する市民の意見が、個人の経験や技術に関する情報の提供によってどのように変化するかを実験的に調査することです。
- **実験方法**: 1,500人以上の労働者を対象に、AIを用いたタスクの割り当てを行い、彼らの態度の変化を追跡。タスクの内容や割り当ての決定者(AIまたは人間)をランダムに変え、3回のパネル調査を実施しました。
- **主な発見**:
- AIを上司として経験した労働者の行動には影響があったが、政策に対する態度には変化が見られなかった。
- AIに関する情報を学んだ労働者は、特にポジティブな情報に対して態度を大きく変える傾向があった。
- AIの使用に対する支持は、特に公共資源の配分に関する政策決定において高まった。
- **具体的な事例**:
- トロント市の「スマートシティ」プロジェクトは、プライバシーや監視に関する懸念から中止された。
- 英国の教育省は、AIアルゴリズムを用いた試験成績の予測を公衆の反発を受けて中止した。
- **結論**: AIの公共政策への導入に関する市民の態度は、個人の経験よりも情報の提供によって大きく変わる可能性がある。特に、AIの利点に関する情報は、政策決定におけるAIの使用を支持する意見を増加させることが示された。
この研究は、AI技術の公共政策への適用に関する市民の理解と意見形成において、情報提供の重要性を強調しています。詳細な情報は、以下のリンクからご覧いただけます:[AIを公共政策に活用する政治的側面](https://isps.yale.edu/sites/default/files/files/acpbw-raviv-10-27-23.pdf)
#### 地方自治体における人工知能の導入:市長の認識
この研究は、オーストラリアとアメリカの市長との半構造化インタビューを通じて、地方自治体における人工知能(AI)システムの導入に関する認識を探求しています。
- **AIの導入分野**: 市長たちは、AIが特に有用であると考える分野として、資産管理、サービスの自動化、データ分析、公共サービスの提供などを挙げています。具体的な事例として、道路維持管理やドローンを用いた建物の点検が紹介されています。
- **AIの有用性**: インタビューでは、AIがルーチン業務の自動化や効率化、生産性向上に寄与することが強調されました。
- **導入の課題**: AI導入における主な課題として、データの偏りや不正確さ、職場文化、倫理的問題、財政管理、リスク管理などが挙げられました。
- **導入の準備状況**: 市長たちは、地方政府がAI導入に向けて十分に準備ができていないと感じており、特に財政的な制約や技術的な知識の不足が障害となっています。
- **今後の展望**: AIの導入に関する計画として、データの質向上、倫理的な運用、ステークホルダーとの連携が重要視されています。
詳細な情報は、以下のリンクからご覧いただけます:[地方自治体における人工知能の導入:市長の認識](https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00146-022-01450-x)
#### 政治的意思決定における人工知能の役割
本研究は、欧州連合(EU)におけるアルゴリズミック意思決定(ADM)システムの使用が、政策決定プロセスの正当性に与える影響を調査しています。
- **正当性の認識**: 参加者は、EUの政治家による従来の意思決定プロセス(HDM)が最も正当性が高いと認識し、ADMシステムのみを使用した場合(ADM)は最も低いと評価しました。
- **透明性と説明責任**: ADMシステムは「ブラックボックス」として扱われ、透明性や説明責任が欠如していると見なされています。
- **実証的な結果**: 研究は、ADMシステムが高品質な出力を生成しても、必ずしも正当性が高まるわけではないことを示しています。
- **政策提言**: EUの政策立案者は、ADMシステムを導入する際には、実際の正当性と市民の認識する正当性の両方を考慮する必要があります。
詳細な情報は、以下のリンクからご覧いただけます:[政治的意思決定における人工知能の役割](https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/data-and-policy/article/artificial-intelligence-for-political-decisionmaking-in-the-european-union-effects-on-citizens-perceptions-of-input-throughput-and-output-legitimacy/E9796EC30B786810ABA8CCD7316DECB6)
🏷 成功事例と失敗事例の比較分析
#### 自治体におけるAIの成功事例と失敗事例の比較分析
地方自治体におけるAIの導入には、成功事例と失敗事例が存在します。成功事例として、サンタクルーズ郡やボストン市の取り組みが挙げられます。サンタクルーズ郡はAIポリシーを早期に採用し、他の政府のモデルとなることを期待されています。ボストン市では、AIを用いて職務記述書を作成するなどの実験が行われ、AIの価値を認識しつつリスクに対処する必要が強調されています。一方、失敗事例としては、ミシガン州の失業保険機関がエラーの多い自動化ソフトウェアにより、多くの人々を誤って告発したケースや、カリフォルニア州とコロラド州でのメディケイドの誤拒否が挙げられます。これらの事例は、AIシステムの透明性や公平性の重要性を示しており、アルゴリズムの誤りが生活に大きな影響を及ぼす可能性があることを警告しています。AIの導入においては、成功を収めるための戦略と同時に、失敗を避けるための慎重なアプローチが求められます。
#### 成功事例と失敗事例の詳細分析
- **成功事例**
- **サンタクルーズ郡**: カリフォルニア州のサンタクルーズ郡は、AIポリシーの早期かつ効果的な採用者の一例です。郡の地区監督官ザック・フレンドは、連邦および州レベルで不足している機会を見出し、サンタクルーズの取り組みが他の政府のモデルとなることを期待しています。具体的には、AIを用いてデータ分析を行い、効率的なリソース配分を実現しています。
- **ボストン市**: ボストン市は、AIを用いて職務記述書を作成するなどの実験を行い、AIの価値を認識しつつリスクに対処する必要が強調されています。この取り組みは、AIの導入が市の運営にどのように寄与するかを示す良い例です。
- **失敗事例**
- **ミシガン州の失業保険機関**: 2013年から2015年にかけて、ミシガン州の失業保険機関がエラーの多い自動化ソフトウェアにより、40,000人を失業保険詐欺で誤って告発しました。この事例は、AIシステムの透明性と正確性の欠如がもたらす深刻な影響を示しています。
- **カリフォルニア州とコロラド州**: 2010年代中頃に、妊婦や養子の子供が誤ったデータや不正確にエンコードされたルールに基づいてメディケイドを拒否される事例が発生しました。これもまた、AIの導入におけるリスクを浮き彫りにしています。
- **AIシステムの透明性と公平性**: AIの導入においては、システムの透明性や公平性が重要です。特に、アルゴリズムの誤りが生活に大きな影響を及ぼす可能性があるため、慎重なアプローチが求められます。
これらの事例から、AIの導入においては成功を収めるための戦略と同時に、失敗を避けるための慎重なアプローチが必要であることが明らかです。AIの活用は、適切に行われれば地方自治体の運営を効率化し、住民サービスの向上に寄与する可能性がありますが、リスク管理も同時に行う必要があります。
詳細な情報は、以下のリンクから確認できます。
- [AIの導入による地方自治体の利点](https://www.futurepolicing.org/blog/the-benefits-of-using-ai-in-municipal-government-a-use-case-overview)
- [人工知能の責任ある利用に関する概要](https://www.aaas.org/programs/epi-center/AI)
- [地方政府の進化の必要性](https://insider.govtech.com/california/news/commentary-local-governments-must-evolve-quickly-in-this-ai-era)
- [AI導入の出発点:都市と州の活用事例](https://www.govtech.com/artificial-intelligence/where-to-start-with-ai-cities-and-states-offer-use-cases)
🏷 AI利用におけるリスクと利点
#### AI利用におけるリスクと利点
AIは、地方政府における公共サービスの提供や市民とのコミュニケーションを改善する可能性を持っています。特に、スタッフ不足や資金不足に直面している地方政府にとって、AIの導入はサービスのアクセス向上や政策参加の促進に寄与することが期待されています。しかし、AIの適切な管理がなされない場合、公共の信頼を損ない、社会的不平等を強化するリスクも伴います。AIの使用には、バイアスの増幅や不適切な使用による信頼性の低下が懸念されており、特に重要な決定にAIを使用する際には注意が必要です。AIは選挙管理や市民の参加を促進する一方で、偽情報の拡散や市民の混乱を引き起こすリスクも存在します。したがって、AIの導入に際しては、慎重な管理と透明性が求められます。
#### AIの影響
AIは米国の選挙や世界中の政治レースに影響を及ぼしています。特に、AIが偽情報を生成・配布する能力に焦点が当てられ、政府はその潜在的な悪影響を制限するための規則や規制を提案しています。AIは選挙情報環境、サイバーセキュリティ、選挙管理に影響を与え、リスクと機会を定義・評価します。例えば、AIツールは偽情報を迅速かつ低コストで生成・配布する能力を持ち、選挙における情報環境に大きな影響を与えます。
#### 政策対応
AIの進展に対する政策は、主にAIによる選挙の偽情報の影響を最小限に抑えることに焦点を当てています。政策立案者は、AIを使用した選挙コミュニケーションにおける禁止や開示を求める法律を提案しています。現在、15州がAI生成の選挙コンテンツに対する開示を義務付けています。
#### 公共の認識と個人の責任
選挙管理者、個々の市民、政治候補者は、AIによる偽情報の影響を制限するために具体的な行動を取る必要があります。信頼できる情報源としての役割を果たし、公共の信頼を築くことが重要です。また、有権者は情報に対して懐疑的であり、複数の情報源を確認することが求められます。
#### リスクと懸念
AIの使用には、バイアスの増幅や不適切な使用による信頼性の低下などのリスクがあります。ボストンでは、自動転写ツールが州法に違反することが判明しました。また、AIの普及がクリエイティブな職業に与える影響についても懸念が示されています。
#### 今後の展望
AIの導入が進む中で、地方政府は新たなガイドラインやポリシーの改訂を行うことが予想されます。AIの利用に関する政治的な対立が、技術の採用や革新に影響を与える可能性も指摘されています。AIは2024年以降の選挙において、選挙インフラ、サイバーセキュリティ、選挙管理に影響を与える可能性があります。
[詳細はこちら](https://www.rstreet.org/research/impact-of-artificial-intelligence-on-elections/)
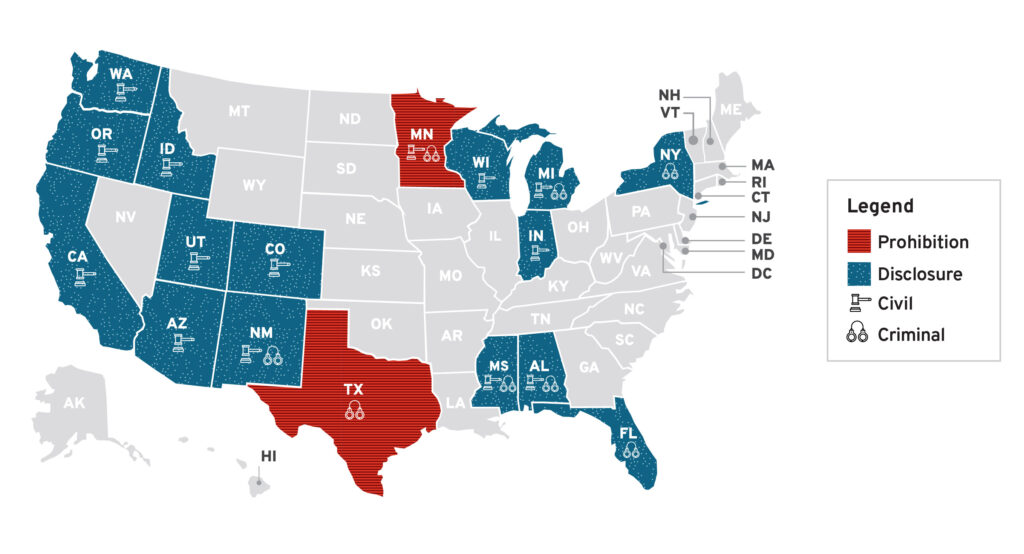
[出典: National Conference of State Legislatures](https://www.ncsl.org/elections-and-campaigns/artificial-intelligence-ai-in-elections-and-campaigns)
[出典: FiscalNote](https://fiscalnote.com/blog/artificial-intelligence-local-government)
[出典: NLC](https://www.nlc.org/article/2023/08/31/exploring-ai-applications-in-city-government-the-promise-and-the-risks/)
[出典: Brookings](https://www.brookings.edu/articles/ai-can-strengthen-u-s-democracy-and-weaken-it/)
🏷 倫理的考慮事項と今後の方向性
#### 倫理的考慮事項と今後の方向性
AIの導入においては、倫理的な考慮事項が重要である。政府機関は、透明性、説明責任、協力を強調する戦略でAIの導入を進めるべきであり、AIが私たちの生活や仕事の仕方を根本的に変える可能性を秘めていることを考慮する特別な責任を負っている。効果的なAI戦略は、組織のビジョンと整合性を持ち、技術的および管理的な視点を取り入れる必要がある。AIの価値を説明する際には、組織とその労働力の視点を含めることが重要であり、AIが仕事を奪うのではなく、既存の役割を強化する方法を示す必要がある。今後、政府はAIの倫理的な考慮事項を含むビジョンを構築し、責任あるAIの使用を推進することが求められる。
#### AIを用いた政治世論調査
AIは、公共世論調査の限界を克服する手段として注目されている。従来の調査方法では、非応答率の増加や真実の隠蔽が問題となっているが、AIはインターネット上の意見を瞬時に調査し、要約する能力を持つ。例えば、米国の選挙サイクルでは、1997年には36%の人が調査に応じていたが、2018年にはその数が6%にまで減少した。このような背景から、AIエージェントが特定の人口統計に基づいて反応することが期待されている。AI調査は、従来の方法と組み合わせて使用されることで、より正確な結果を得る可能性がある。
詳細な情報は、[こちら](https://ash.harvard.edu/publications/using-ai-political-polling)から確認できます。
#### 地方自治体におけるAIの活用事例
地方自治体では、AI技術を活用してプロセスを効率化し、住民を支援する事例が増えている。例えば、オーストラリアのシドニー市では、AIを用いた申請プロセスを導入し、申請者に即時フィードバックを提供している。また、カナダのロンドン市では、AIツールを用いてホームレスの予測と防止を行い、93%の成功率を記録した。台湾の桃園市では、AI搭載の街灯がエネルギー効率を向上させるために導入され、電力使用を約12%削減している。
詳細な情報は、[こちら](https://lgiu.org/blog-article/ai-and-the-council-case-studies-and-resources-for-local-government/)から確認できます。
#### AI戦略の構築
政府機関は、AIを活用するための包括的な戦略を持つべきである。シカゴ市では、犯罪を未然に防ぐためにアルゴリズムを使用し、ピッツバーグではAIを用いた信号機が交通時間を25%短縮した。AIは新たな洞察や予測を生み出し、市民との新しいインタラクションを創出する可能性を秘めているが、効果的な戦略が必要である。最近の調査によると、回答した企業の半数がAIを優先事項と考えているが、広範なAI戦略を持っているのは25%に過ぎない。
詳細な情報は、[Deloitte Insights](https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/public-sector/ai-strategy-for-government-leaders.html)で確認できます。
#### 政府AI連合
サンノゼ市の政府AI連合は、AIガバナンスプログラムを推進し、責任あるAIの使用を提唱している。具体的には、効果的なAIの使用事例を共有し、AI技術の適切な導入を目指しているが、詳細な情報は現在アクセスが制限されているため、確認が難しい。
詳細な情報は、以下のリンクから確認できますが、現在アクセスが制限されています:[サンノゼ市のAI連合](http://www.sanjoseca.gov/your-government/departments-offices/information-technology/ai-reviews-algorithm-register/govai-coalition)
🖍 考察
### 調査の結果
自治体におけるAIの政治利用事例は、成功事例と失敗事例が存在します。成功事例としては、サンタクルーズ郡やボストン市が挙げられ、AIポリシーの早期採用や職務記述書の作成において実験的な取り組みが行われています。一方、失敗事例としては、ミシガン州の失業保険機関による誤った告発や、カリフォルニア州とコロラド州でのメディケイドの誤拒否があり、これらはAIシステムの透明性や公平性の重要性を示しています。AIの導入は公共サービスの提供や市民とのコミュニケーションを改善する可能性を持っていますが、適切な管理がなされない場合、公共の信頼を損ない、社会的不平等を強化するリスクも伴います。
### 推定
調査の結果から、以下の問題が解明されていないことがわかります。
1. AIの導入における市民の信頼構築の方法
2. 失敗事例から得られる教訓の具体化
3. AIの倫理的な考慮事項の実践的な適用
これらの問題を細分化し、推定を行います。
1. **市民の信頼構築の方法**
- 情報提供の透明性を高めることで市民の理解を促進する。
- 市民参加型のプロジェクトを通じて、AIの利用に対する支持を得る。
2. **失敗事例からの教訓**
- 失敗事例の分析を通じて、AIシステムの設計段階でのリスク評価を強化する。
- 失敗事例を公開し、他の自治体が同様の過ちを避けるための教育資源とする。
3. **倫理的な考慮事項の適用**
- AI導入に際して、倫理的なガイドラインを策定し、実施するためのフレームワークを構築する。
- 定期的な評価とフィードバックを通じて、AIの使用が倫理的に行われているかを監視する。
これらの推定を組み合わせることで、AIの導入において市民の信頼を得るための戦略が明確になります。
### 分析
調査の結果と推定を基に、自治体におけるAIの政治利用について多角的に分析します。成功事例は市民の信頼を得るためのモデルとなり得ますが、失敗事例はその逆で、透明性や公平性の欠如が信頼を損なう要因となります。AIの導入においては、情報提供の重要性が強調されており、これが市民の理解と支持を促進する鍵となります。
また、AIの倫理的な考慮は、今後の政策決定において重要な要素であり、自治体は市民との信頼関係を築くために、透明性と説明責任を重視する必要があります。AIが公共サービスの質を向上させる一方で、適切な管理がなされない場合のリスクも考慮しなければなりません。
### 今後の調査
今回の調査における限界点を振り返ると、具体的な事例の数が限られていることや、AIの導入に関する市民の意見が十分に反映されていないことが挙げられます。次の行動計画として、以下の調査テーマを提案します。
- AI導入における市民の信頼構築に関する調査
- 失敗事例からの教訓を活かしたAI政策の改善策
- 自治体におけるAIの倫理的ガイドラインの策定と実施状況の評価
- AIの導入が市民参加に与える影響に関する調査
- 他国の成功事例と失敗事例の比較分析
📚 参考文献
参考文献の詳細は、ブラウザでページを表示してご確認ください。