📜 要約
### 主題と目的の要約
今回の調査では、年齢や性別などの条件による鬱の発症率の違いに焦点を当て、アメリカの成人におけるうつ病と生活の質の関係について調査しました。特に女性が男性よりもうつ病にかかりやすいことや、年齢層による鬱の発症率の差異について明らかにしました。
### 主要な内容と発見
- 女性の方が男性よりもうつ病にかかりやすいことが示されており、特に40歳から64歳と65歳以上の女性の身体的側面の生活の質スコアが低いことが明らかになりました。
- 1990年から2019年までの研究では、女性の方が男性よりもMDDのリスクが高く、特に若い年齢層や発展した国々で性差が大きいことが報告されています。
- 環境要因と抑うつの関連性についての研究では、遺伝要因と環境要因が抑うつのリスクに影響を与えることが示されました。特に子供時代のストレスや母親の抑うつが重要な要因とされています。
### 結果と結論のまとめ
今回の調査から、女性が男性よりもうつ病にかかりやすいことや、年齢や環境要因が鬱の発症率に影響を与えることが明らかになりました。これらの結果は、うつ病の予防や治療において、性別や年齢、環境要因を考慮する重要性を示唆しています。
🔍 詳細
🏷 年齢と性別による鬱の発症率の差異
#### アメリカの成人におけるうつ病と生活の質の関係における年齢と性別の違い
アメリカの成人におけるうつ病と生活の質の関係における年齢と性別の違いを調査した研究では、うつ病のある人はQoLのスコアが低く、女性は男性よりもQoLのスコアが低いことが示された。特に女性のうつ病患者は40歳から64歳と65歳以上で身体的側面のQoLスコアが低かった。
[研究リンク](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8260438/)
#### 性差と女性におけるうつ病の要因
男女間のうつ病における性差についてのメタ分析では、大うつ病の診断においてOR = 1.95、うつ病症状においてd = 0.27であり、性差は思春期にピークに達し、その後減少して成人期において安定している。女性におけるうつ病の高い発生率は、ホルモンの違い、社会化の違い、社会的役割、ストレスの生活イベントなどの要因によるものと考えられる。特に女性は生殖年齢におけるホルモンのリスク要因や社会的役割の影響を受けやすく、ストレスの生活イベントに対する感受性が高い可能性がある。
[NCBIで続きを読む](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=28447828)

#### 年齢と性別による鬱の発症率の差異
年齢と性別による鬱の発症率の差異に関する研究から、女性の方が男性よりもうつ病にかかりやすいことが示されている。1990年から2019年にかけて、女性の方が男性よりもMDDのリスクが高かったことが報告されており、若い年齢層やより発展した国々でより大きな性差が見られた。
#### 年齢と性別による鬱の発症率の差異に関する考察
性差の改善がわずかに進展しているものの、過去数十年間にわたり性差は依然として存在し、女性の方が常に男性よりも高い発症率を示している。若い年齢層やより発展した国々でより大きな性差が見られることから、性差によってうつ病の遺伝的根拠に影響を与える要因が異なる可能性がある。これらの結果は、MDD発症率の性差を減らすための性別特有の健康政策の重要性を強調している。
#### 年齢と性別による鬱の発症率の差異に関する詳細情報
- [NCBIの記事リンク](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3847538/)
- [Frontiersの記事リンク](https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/genetics/articles/10.3389/fgene.2020.562316/full)
- [Biomed Centralの論文リンク](https://annals-general-psychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12991-023-00486-7)
- [ScienceDirectの記事リンク](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1049386721000098)
- [McLean Hospitalの記事リンク](https://www.mcleanhospital.org/essential/impact-age-and-gender-mental-health)









🏷 環境要因と鬱の関連性
#### 環境要因と抑うつの関連性
環境要因と抑うつの関連性についての研究では、遺伝要因が抑うつの脆弱性の37-48%を占める一方、環境要因が残りの影響の半分以上を占める可能性がある。環境要因は全ての年齢層における抑うつの潜在的なリスク要因の大部分を占めており、子供時代のストレスや母親の抑うつが重要な要因とされている。
#### 環境要因と抑うつの影響
環境要因は抑うつのリスク要因と影響において重要であり、子供時代のストレスや母親の抑うつが抑うつの発症に影響を与える可能性が高い。遺伝要因と環境要因の相互作用が抑うつのリスクを予測する上で重要であり、環境要因の影響は遺伝的感受性と組み合わさることで抑うつの発症率に影響を与える。環境要因の理解と対処は抑うつの予防や治療において重要である。
#### Urban-Rural Differences in the Prevalence of Depressive Symptoms in Korean Adults
この研究は、2017年の韓国コミュニティ健康調査からの216,765人の参加者を対象に、都市部と地方部に住む韓国人のうつ病の有病率を調査した。都市部の調査対象者の調整有病率は3.33%であり、地方部は2.59%であった。都市部のうつ病有病率は地方部よりも1.29倍高かった。都市部と地方部のうつ病有病率の差は、収入水準によって異なり、低所得者層ではより顕著であった。性別、年齢、教育レベルによって都市部と地方部のうつ病有病率の差は変わらなかった。
[論文リンク](http://doi.org/10.4068%2Fcmj.2023.59.2.128)

#### 都市の土地利用とうつ病症状の関連性についての研究
この研究は、都市の生活環境を表す土地利用が精神的健康に与える影響を調査しました。都市の土地利用と若者のうつ病症状との関連を調査し、異なる土地利用環境を持つ参加者を区別しました。線形エラスティックネット罰則回帰とXGBoostを使用して、都市の土地利用とうつ病症状の線形および非線形関係を明らかにしました。
[詳細なコンテンツはこちらをご覧ください。](https://www.nature.com/articles/s41370-023-00619-w)

🏷 社会的支援と鬱の発症率
#### 米国におけるうつ病診断率の増加と影響要因
米国ではうつ病の診断率が過去最高に達し、特に女性、若者、黒人、ヒスパニックの成人に影響が大きいことが報告されています。女性の診断率は男性を上回り、18歳から29歳のグループが最も高い結果となっています。社会的支援や健康的なライフスタイルがうつ病と関連しており、COVID-19パンデミック後に急激な増加が見られることが指摘されています。
[Gallup News - 米国のうつ病率が過去最高に達する](https://news.gallup.com/poll/505745/depression-rates-reach-new-highs.aspx)
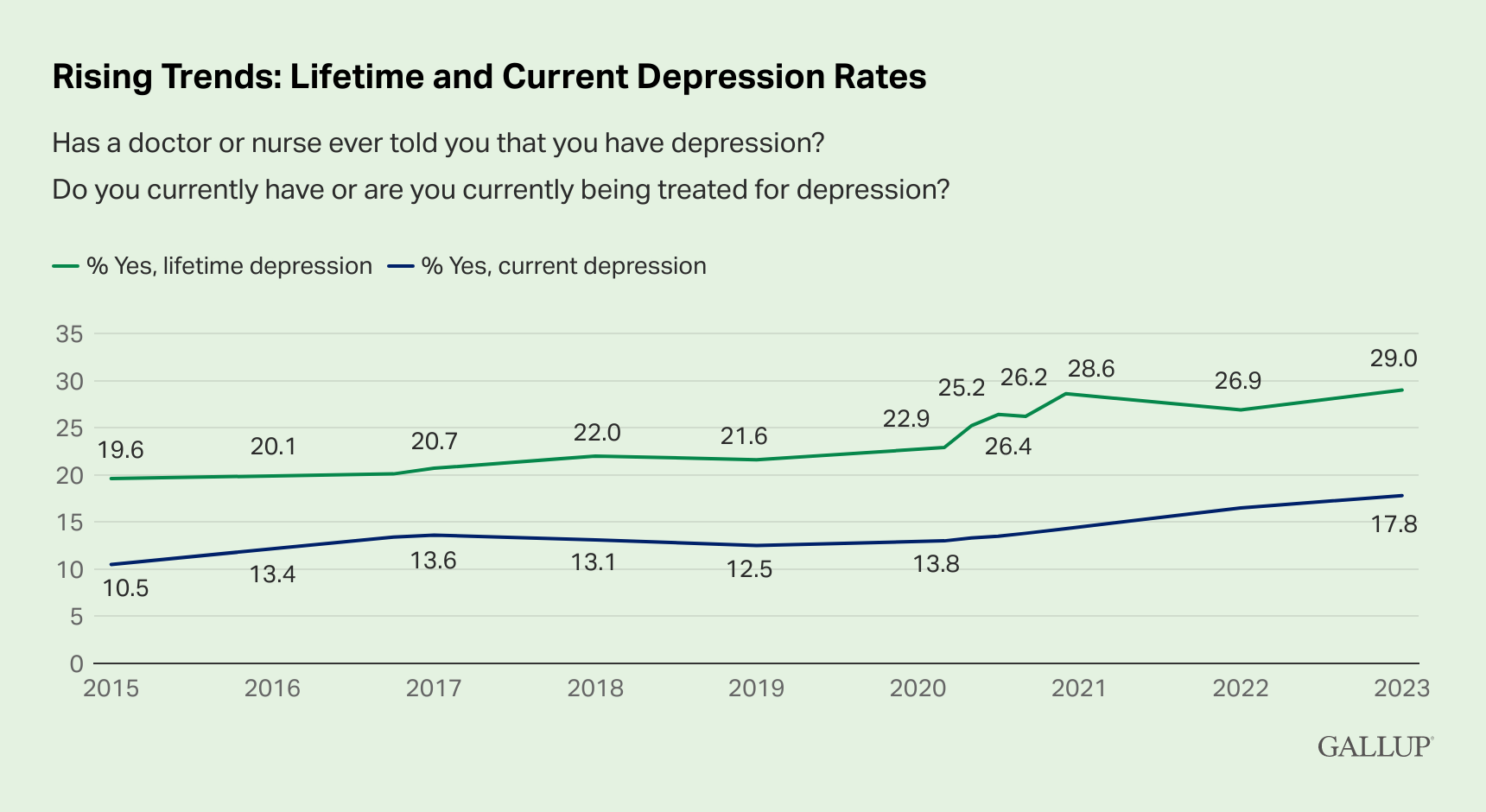
#### 米国におけるうつ病増加の背景と今後の課題
米国では女性、若者、黒人、ヒスパニックの成人におけるうつ病診断率が増加しており、社会的支援や健康的なライフスタイルが重要な要因となっています。COVID-19パンデミック後に急激な増加が見られることから、孤独感や恐怖などの要因がうつ病の増加に影響している可能性が高いと考えられています。今後は社会的支援の重要性を再確認し、適切な支援体制の構築が求められるでしょう。
#### 中国の大学生におけるうつ病と社会的サポート、健康的なライフスタイルの関連性
中国の大学生を対象に行われた調査では、うつ病の有病率が29.8%であり、社会的サポートと健康的なライフスタイルがうつ病と関連していることが示されています。特に女性であること、不十分な社会的サポート、栄養不良、自己実現の欠如がうつ病と有意に関連していることが報告されています。
[BMJ Open - うつ病と社会的サポート、健康的なライフスタイルとの関連性](https://bmjopen.bmj.com/content/11/7/e044236)

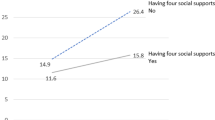
#### COVID-19パンデミック中の社会的支援とうつ病
COVID-19パンデミック中、世界中でうつ病の発症率が上昇しています。社会的支援はうつ病に対する保護要因として確立されており、感情的/情報的支援やポジティブな社会的相互作用がうつ病と強く関連しています。さらなる研究が必要であり、社会的支援の異なるサブタイプがうつ病リスクにどのように影響するかを理解することが重要です。
[Nature - Social support and depression during a global crisis](https://www.nature.com/articles/s44220-023-00078-0)
🏷 労働環境と鬱の関連性
#### 労働環境と鬱の関連性についての要約
労働環境と鬱の関連性についての研究では、産業別のうつ病発生率の違いが示され、高い発生率を示す産業はストレスが高く身体活動が低い傾向があることが明らかになった。長時間労働や職業ストレスがうつ病と関連しており、長時間労働者は精神的健康の悪化が高い割合で報告されている。
#### 労働環境と鬱の関連性についての考察
労働環境と鬱の関連性に関する研究から、職場のストレスや長時間労働がうつ病の発症率に影響を与えることが示されている。特に、高ストレスで身体活動が低い産業や長時間労働者は、うつ病のリスクが高いことが明らかになっている。これらの結果は、労働環境改善や労働時間の適正化が重要であり、労働者のメンタルヘルスを保護するための取り組みが必要であることを示唆している。
#### Prevalence rates for depression by industry: a claims database analysis
- [PMCでの詳細を読む](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4557731/)

#### 長時間労働がうつ病とメンタルウェルビーイングに与える影響...
- [詳細はこちら](http://doi.org/10.3390%2Fijerph16244980)

#### 長時間労働、職業ストレス、およびウェルビーイングの影響についての研究
- [研究のリンク](https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.797882/full)

#### Depression | Workplace Health Strategies by Condition | CDC
- [参照元リンク](https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/depression/default.html)
🏷 鬱の発症率に影響を与える複数の要因
#### 抑うつの発症率に影響を与える複数の要因
抑うつの発症率に影響を与える複数の要因には、遺伝子、エピジェネティック因子、環境条件、ストレス、栄養不足、幼少期のストレスや虐待などが含まれる。遺伝子の変異(SLC6A4、COMT、TPH2、FKBP5、MDD1、HTR2A、MDD2)が特定され、エピジェネティック変化は治療アプローチに新たな可能性をもたらす。
#### 抑うつの発症率に影響を与える要因の考察
抑うつの発症率には遺伝子、エピジェネティック因子、環境要因が関与しており、それらの相互作用が重要である。遺伝子の変異やエピジェネティック変化が抑うつのリスクを増加させる可能性があり、環境要因も重要な役割を果たす。遺伝子-環境相互作用の研究は、抑うつの遺伝学を理解する上で重要であり、個々の要因だけでなく複合的な影響も考慮する必要がある。
#### 遺伝とエピジェネティクスによる抑うつの影響
抑うつに関連する遺伝子やエピジェネティック因子は、環境と相互作用し、抑うつの発症率に影響を与える重要な要素です。遺伝子の変異やエピジェネティック変化が抑うつのリスクを増加させる可能性があり、これらの要因を理解することは治療アプローチの改善につながるでしょう。

[詳細を読む](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9232544/)
#### 遺伝子-環境相互作用とうつ病の遺伝学
うつ病の遺伝学は、遺伝子と環境の相互作用によって影響を受けています。遺伝子発現の変動や遺伝子型と環境の相関、遺伝子変異と環境変数の関係などが研究されており、個人差や環境要因がうつ病の発症にどのように影響するかが明らかになっています。
- [Gene–environment interaction and the genetics of depression - PMC](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC400687/)
###
###
🖍 考察
### 結果の確認
調査から得られた主要な結果を振り返ると、女性の方が男性よりもうつ病の発症率が高いことが確認されています。性差は思春期にピークに達し、その後減少して成人期において安定していることも示されています。また、若い年齢層やより発展した国々で性差がより大きく見られることが報告されています。
これらの結果は、女性の方が男性よりもうつ病になりやすいという一般的な傾向を裏付けるものであり、性差がうつ病の遺伝的根拠に影響を与える可能性があることを示唆しています。
### 重要性と影響の分析
得られた結果は非常に重要であり、性差がうつ病の発症率に与える影響を考える上で重要な示唆を提供しています。特に、女性におけるうつ病の高い発生率は、ホルモンの違いや社会的要因などによるものと考えられ、性差がうつ病の遺伝的根拠に影響を与える可能性があることが示唆されています。
これらの結果は、性差によってうつ病の予防や治療において性別特有のアプローチが必要であることを示唆しており、性差を考慮した健康政策の重要性を強調しています。
### ネクストステップの提案
調査から生じた疑問点や未解決の課題に対処するために、性差がうつ病の遺伝的根拠にどのように影響を与えるのかをさらに詳しく調査することが重要です。また、性差を考慮したうつ病の予防や治療法の開発に向けた研究が必要です。
次の行動計画として、性差がうつ病に与える影響をさらに探究し、性別特有のアプローチを取り入れた健康政策の策定を推進することが重要です。
### 今後の調査の方向性
今回の調査における限界点を踏まえると、性差がうつ病の遺伝的根拠に与える影響をより詳しく理解するための研究が必要です。さらに、性差を考慮したうつ病の予防や治療法に関する研究を進めることで、より効果的なアプローチを見つけることができるでしょう。
📚 参考文献
参考文献の詳細は、ブラウザでページを表示してご確認ください。